Most homeowners experience frustrating slowdowns in their home network at some point, often leaving you unable to stream, game, or work efficiently. Various factors contribute to this issue, including outdated equipment, network congestion, and interference. Understanding the reasons behind these slow speeds is the first step towards improving your connection. This guide will help you identify common culprits and provide practical solutions that can enhance your network performance, ensuring you enjoy a seamless online experience.
Key Takeaways:
- Network congestion from multiple devices can lead to slower speeds; consider limiting active connections or upgrading your router.
- Distance from the router and physical obstructions can weaken the signal; reposition the router or use extenders to improve coverage.
- Interference from other electronic devices can impact performance; keep the router away from microwaves and cordless phones for better reliability.
Understanding Your Home Network
Your home network comprises various devices that connect through a router to access the internet. It typically includes computers, smartphones, smart TVs, and IoT devices. Each component plays a role in creating your digital ecosystem, impacting your overall network performance. By understanding this, you can identify potential issues influencing your internet speed.
Common Causes of Slowdowns
Slowdowns can arise from multiple sources, including network congestion from too many connected devices, outdated hardware, interference from other electronics, and suboptimal router placement. Additionally, issues with your internet service provider can contribute significantly to reduced speeds, making it vital to assess both your internal and external factors.
Types of Home Networks
Home networks can be categorized into wired and wireless configurations. Wired networks use Ethernet cables for direct connections, providing stable and fast speeds. In contrast, wireless networks utilize Wi-Fi, offering mobility and convenience but may experience interference and signal loss. You might also encounter hybrid setups combining both methods for optimal performance.
| Type | Description |
| Wired | Utilizes Ethernet cables, offering high speed and stability. |
| Wireless | Connects devices via Wi-Fi, providing mobility but less reliability. |
| Mesh | Multiple nodes that blanket your home in Wi-Fi. |
| Powerline | Transmits data through electrical wiring for improved connectivity. |
| Hybrid | Combines wired and wireless for balanced performance. |
Wired networks often excel in speed and reduce latency, making them ideal for gaming and heavy downloads. Conversely, wireless networks are advantageous for mobility, allowing devices like smartphones and tablets to connect seamlessly. Therefore, your choice will depend on your specific needs and the layout of your living space. Any mix of these types can be tailored to achieve optimal performance.
| Network Type | Use Case |
| Wired | Best for stable, high-speed connections; ideal for desktops and gaming consoles. |
| Wireless | Great for mobile devices; easy setup and flexibility. |
| Mesh | Effective coverage in larger homes or buildings; eliminates dead zones. |
| Powerline | Useful in hard-to-reach areas without Wi-Fi signals; leverages existing electrical wiring. |
| Hybrid | Combines the benefits of wired and wireless; offers versatility and performance. |
Identifying Speed Issues
To tackle slow network speeds, you first need to pinpoint where the issue lies. Start by assessing whether the slowdown occurs across all devices or just one. Identify if the issue arises during specific times of day, which could indicate network congestion, or if it’s consistently poor regardless of traffic. By narrowing down the timeframes and devices affected, you can better diagnose whether it’s an internet service provider issue or something within your home network setup.
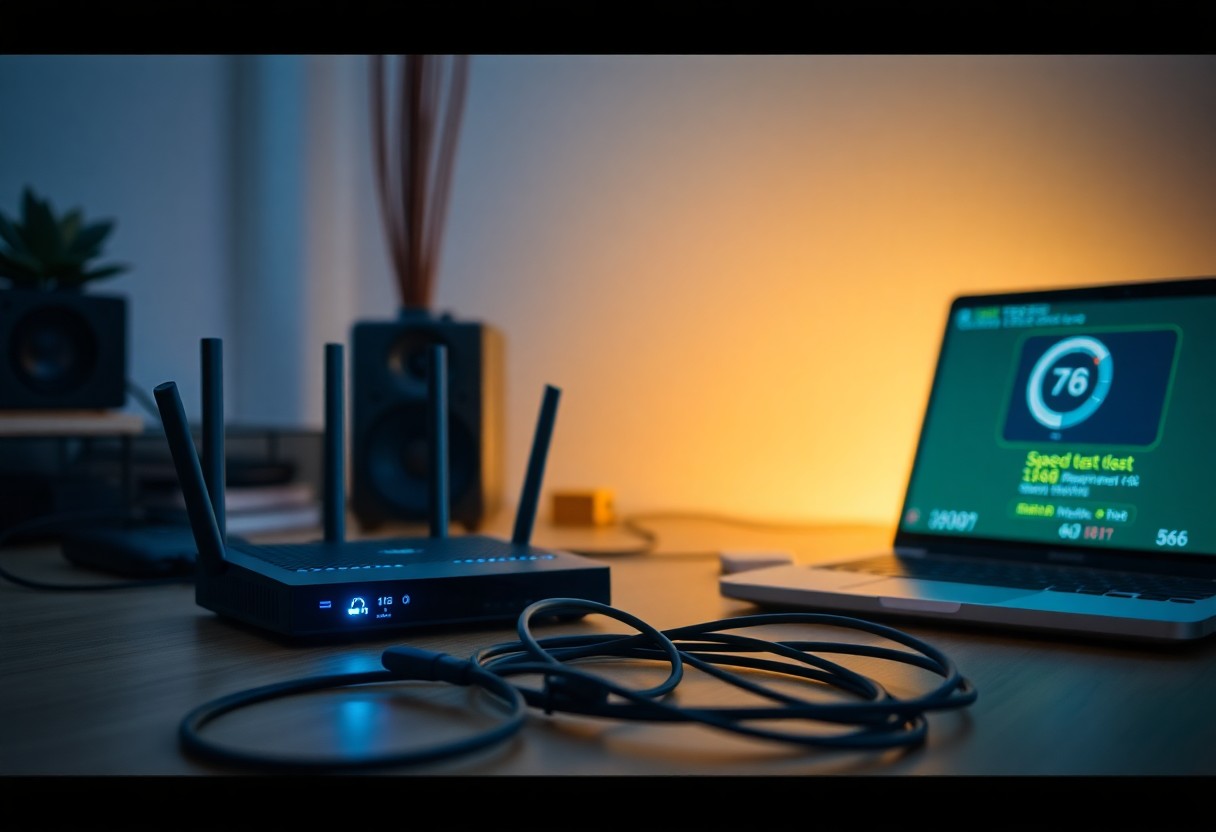
Testing Your Internet Speed
Begin your investigation by testing your internet speed using reliable online tools such as Speedtest by Ookla or Fast.com. Conduct these tests at various times of the day to understand fluctuations in performance. Check the speed against what you’re paying for to see if you’re receiving the expected bandwidth. If the results are significantly lower, it’s time to explore potential causes.
Device Limitations and Interference
Your devices can significantly limit your network speed, especially if they are outdated or not optimized. Old routers may struggle with newer technology demands or have a lower maximum data rate. Additionally, interfering appliances, such as microwaves or cordless phones, can reduce performance by disrupting the wireless signal, especially on the 2.4 GHz band. Ensuring your router is updated and positioned away from potential interferences can greatly enhance your network’s efficiency.
Evaluating device limitations involves checking the specifications of each device connected to your network. For example, if you’re using a dual-band router, ensure your devices support the 5 GHz band for faster speeds, which also suffers less interference than the 2.4 GHz band. Inspect your network devices for performance rankings or reviews to identify any that may be bottlenecks. Replacing aging or underperforming hardware with modern alternatives can lead to significant improvements, enabling your network to handle more connections and higher speeds efficiently.
Router Optimization
Your router plays a significant role in the speed and reliability of your home network. By optimizing its settings and placement, you can enhance performance and diminish sluggishness. Simple adjustments, such as changing your Wi-Fi channel or enabling Quality of Service (QoS), can prioritize bandwidth for your most critical devices, ensuring a smoother online experience.
Placement and Configuration
The physical location of your router greatly impacts signal strength and coverage. Position your router in a central area of your home, elevated off the ground, and away from walls and obstructions. Additionally, configure your router settings to utilize the latest wireless standards (like 802.11ac or 802.11ax), and consider using the 5GHz band for devices that require higher speeds over shorter distances.
Firmware Updates
Keeping your router’s firmware updated is imperative for maintaining optimal performance and security. Manufacturers regularly release updates that can fix bugs, enhance functionality, and improve speed. Check your router’s administration interface for update options, and set reminders to perform this task routinely.
Regular firmware updates are critical not just for speed but also for security. Vulnerabilities in outdated software can expose your network to intrusions and attacks. For instance, updated firmware may provide patches for potential exploits or improve compatibility with newer devices. Many routers now support automatic updates, so enabling this feature can simplify the process and ensure you’re benefiting from the latest enhancements without manual intervention.
Network Traffic Management
Network traffic management optimizes performance by controlling the flow and prioritization of data across your home network. Effective management ensures that critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth during peak usage times, preventing slowdowns and buffering when you need speed the most. Implementing quality of service (QoS) settings on your router can significantly enhance your home internet experience, allowing you to customize preferences based on the specific needs of different devices and applications.
Bandwidth Allocation
Allocating bandwidth is vital for ensuring that your most important devices get the speed they require. By configuring your router’s QoS settings, you can assign higher priority to activities like streaming or gaming, which can enhance performance. For example, set your gaming console or work laptop to receive more bandwidth during critical usage times, thus minimizing lag and interruptions.
Managing Connected Devices
With numerous devices connected to your network, managing them effectively can prevent congestion and enhance performance. Regularly evaluate the devices linked to your network and identify any unauthorized access or those consuming excessive bandwidth. Consider implementing restrictions or managing schedules for devices that may not be in use during peak hours, ensuring that vital applications run smoothly.
Monitoring connected devices involves regularly checking your router’s settings to identify which devices are online and how much bandwidth they utilize. You can use network management tools that help visualize traffic, enabling you to pinpoint any device causing issues. For instance, if a smart refrigerator is using significant bandwidth for updates, you can schedule those updates for off-peak hours. This proactive approach allows your primary devices to function optimally without the interference of lower-priority connections.
Upgrading Your Equipment
Your equipment significantly influences your network’s performance, making upgrades a powerful solution for combating slow speeds. Often, older routers or outdated modems can’t keep up with the demands of modern devices and high-speed internet plans. Investing in newer models that support the latest Wi-Fi standards, like Wi-Fi 6, can enhance both speed and coverage in your home.
When to Upgrade Your Router
Choosing the Right ISP Plan
Your internet service provider plan directly impacts your network’s performance. Evaluate your usage requirements, such as streaming, gaming, or working from home, to select a plan that meets your household’s needs. If your current speed feels insufficient, consider options that offer higher bandwidth to accommodate multiple users and devices simultaneously.
Choosing the right ISP plan involves understanding not only your current bandwidth usage but also future demands. Many households today leverage multiple devices streaming high-definition content or engaging in online gaming, which necessitates higher speeds. For example, a plan offering 200 Mbps might suffice for casual browsing, but for a family with several heavy internet users, a package with 500 Mbps or more ensures smooth performance without buffering or lag. Evaluating your usage patterns can help you select a plan that secures optimal speed, reducing frustration and improving your overall internet experience.
Securing Your Network
Strengthening your network’s security is necessary to maintaining performance and protecting your personal information from cyber threats. Without proper safeguards, your devices can become easy targets for hackers, resulting in data breaches, identity theft, and compromised bandwidth.
Importance of Network Security
Your home network serves as a gateway to the internet, and its security directly impacts not just your device safety, but also your privacy. When unsecured, your network is vulnerable to unauthorized access, which can slow down your connection and expose sensitive data.
Best Practices for Securing Wi-Fi
To effectively secure your Wi-Fi, start by changing the default SSID and creating a strong password. Utilize WPA3 encryption for enhanced security, disable WPS, and consider hiding your network SSID to make it less visible. Regularly update your router’s firmware to patch vulnerabilities and establish a guest network for visitors to prevent unauthorized access to your main network.
Implementing these best practices can significantly reduce risks associated with network breaches. Strong passwords should combine letters, numbers, and symbols, ensuring they are not easily guessable. Disabling the WPS feature is vital, as it poses a risk due to vulnerabilities which hackers can exploit. Additionally, updating your router’s firmware not only secures your network but also optimizes performance. Guest networks can isolate your main network from potential threats introduced by temporary visitors, allowing you to safeguard your data while providing access. Regularly revisiting these security measures ensures ongoing protection against emerging cyber threats.
Final Words
Drawing together the insights shared, it’s clear that several factors can contribute to your home network slowing down. By assessing your devices, optimizing your Wi-Fi settings, and considering interference, you can significantly enhance your network’s performance. For specific issues like device-specific troubles, check out this resource on Why is my Wifi often slow and cutting out on only one device?. Implement these strategies to enjoy a faster, more reliable connection.
FAQ
Q: What are common reasons for my home network slowing down?
A: Several factors can contribute to a slow home network, including outdated equipment, excessive connected devices, interference from other electronics, and issues with your Internet Service Provider (ISP). Ensuring your router’s firmware is updated and regularly rebooting your modem can also help maintain speed.
Q: How can I improve my Wi-Fi signal strength at home?
A: To enhance your Wi-Fi signal, try repositioning your router to a central location, eliminating physical obstructions, and changing the frequency band from 2.4 GHz to 5 GHz for devices that support it. Additionally, consider investing in Wi-Fi extenders or mesh systems for larger spaces.
Q: What steps can I take to manage bandwidth usage effectively?
A: To manage bandwidth, prioritize vital devices and applications using Quality of Service (QoS) settings on your router. Regularly check for unauthorized devices connected to your network, and consider limiting the upload/download speeds for certain devices that are not in use.